Hi,
I did some change (again) in the load function to improve the speed when you're load some big data file but you want use only some columns. I did all my tests with a file with 9722 line and 16 columns.
The bench test file is after.
I think that the result of the bench are interesting:
I you want use 2 columns on the 16 the results are:
load matplotlib 0.58
load with columns choice 0.27
normal load inside the new load version 0.58
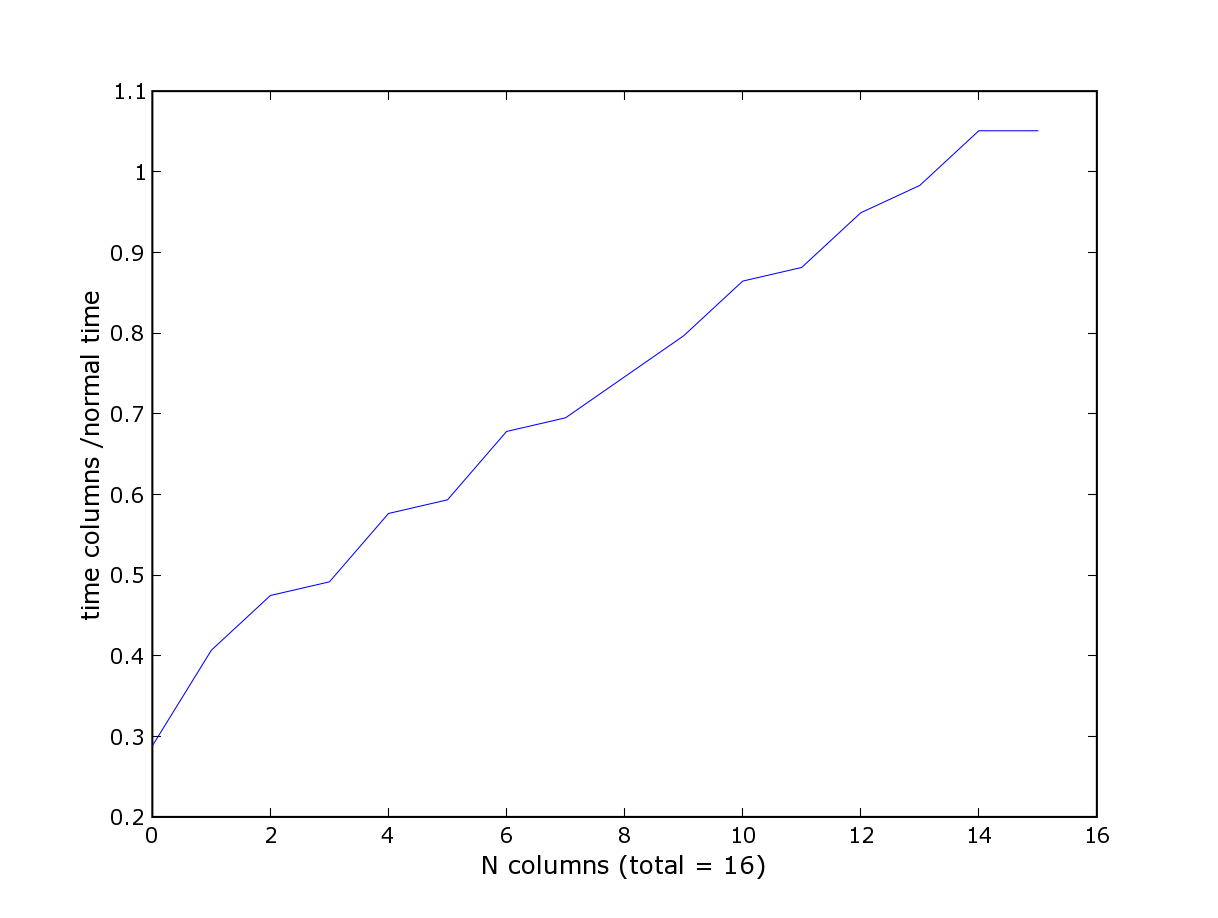
We win a factor two. I know that depend totally from the number of columns and that the change is not interesting and more decrease the efficiency if you want use all the data in your file but like the columns call is optionnal I don't think that is point is crucial but I add a figure to see the effect when you go to one to all the columns.
The load function is after.
Regards,
Nicolas
···
-----------------------------------------------
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from time import clock
t3 = clock()
import load_2
Y=load_2.load('data')
x=Y[:,0]
y=Y[:,1]
t4 = clock()
#print t4-t3
#print x,y
col = [0,6]
t1 = clock()
import load_matplotlib
X=load_matplotlib.load('data')
#X = [X[:,i] for i in col]
x=X[:,0]
y=X[:,1]
t2 = clock()
print 'load matplotlib', t2-t1
#print X
t3 = clock()
import load_2
X=load_2.load('data',columns=range(14))
x=Y[:,0]
y=Y[:,1]
t4 = clock()
print 'load with columns choice', t4-t3
t3 = clock()
import load_2
Y=load_2.load('data')
x=Y[:,0]
y=Y[:,1]
t4 = clock()
normal = t4-t3
print 'normal load ', normal
time = []
for i in range(16):
t3 = clock()
import load_2
X=load_2.load('data',columns=range(i))
x=Y[:,0]
y=Y[:,1]
t4 = clock()
#print 'load with columns choice', t4-t3
time.append(t4-t3)
from pylab import *
time = array(time)/normal
plot(range(16),time)
xlabel('N columns (total = 16)')
ylabel('time columns /normal time')
show()
------------------------------------------------------------------
def load(fname,comments='%',columns=None):
"""
Load ASCII data from fname into an array and return the array.
The data must be regular, same number of values in every row
fname can be a filename or a file handle.
A character for to delimit the comments can be use (optional),
the default is the matlab character '%'.
An second optional argument can be add, to tell which columns you
want use in the file. This arguments is a list who contains the
number of columns beggining by 0 (python style).
matfile data is not currently supported, but see
Nigel Wade's matfile ftp://ion.le.ac.uk/matfile/matfile.tar.gz
Example usage:
X = load('test.dat') # data in two columns
t = X[:,0]
y = X[:,1]
Alternatively, you can do
t,y = transpose(load('test.dat')) # for two column data
X = load('test.dat',[0,2]) # data in two columns (columns 1 and 3 use in the file)
X = load('test.dat') # a matrix of data
X = load('test.dat',columns=[2,3]) # a matrix of data, only columns 3 and 4 will be use
x = load('test.dat') # a single column of data
x = load('test.dat,'#') # the character use like a comment delimiter is '#'
"""
# from numarray import array
fh = file(fname)
X = []
numCols = None
if columns is None:
for line in fh:
line = line[:line.find(comments)].strip()
if not len(line): continue
row = [float(val) for val in line.split()]
thisLen = len(row)
if numCols is not None and thisLen != numCols:
raise ValueError('All rows must have the same number of columns')
X.append(row) else:
for line in fh:
line = line[:line.find(comments)].strip()
if not len(line): continue
row = [val for val in line.split()]
row = [float(row[i]) for i in columns]
thisLen = len(row)
if numCols is not None and thisLen != numCols:
raise ValueError('All rows must have the same number of columns')
X.append(row)
X = array(X)
r,c = X.shape
if r==1 or c==1:
X.shape = max([r,c]),
return X